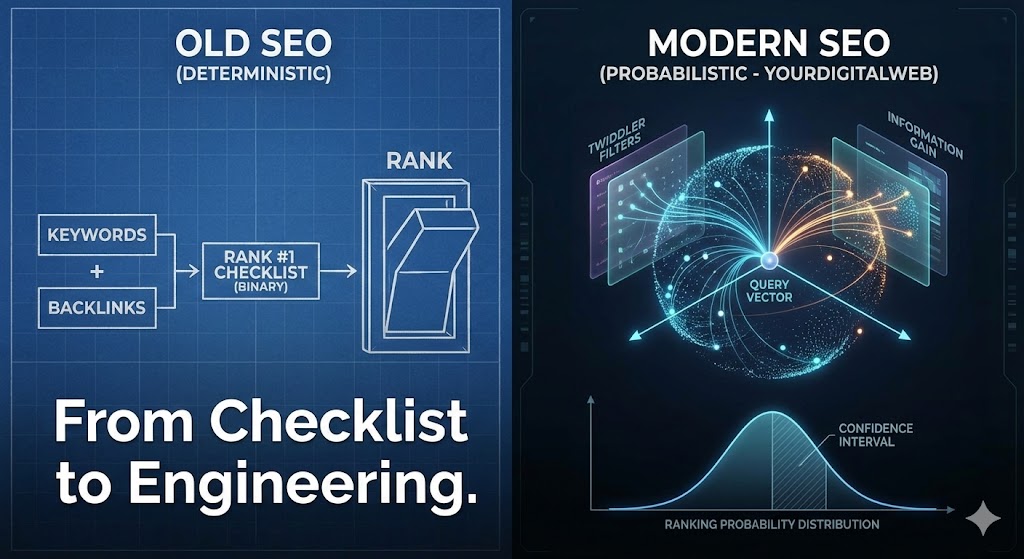
In the early days of search, SEO was comfortably deterministic. It followed a linear logic: Input A (Keywords) + Input B (Backlinks) = Output C (Ranking).
If you didn’t rank, you could audit the inputs, find the missing variable, and fix the output. It was an equation.
Today, SEO is no longer an equation. It is a probability distribution.
With the integration of Deep Learning models (RankBrain, BERT, MUM) and the recent shift towards Neural Information Retrieval, Google has moved from a rule-based sorting engine to a stochastic system.
At YourDigitalWeb, we have fundamentally altered how we audit Enterprise websites. We no longer look for “errors” in a checklist; we analyze Ranking Probability within Google’s Vector Space.
Here is the advanced technical reality of why your site fluctuates, why “best practices” often fail, and how we engineer for uncertainty.
1. The Shift: From Boolean Logic to Vector Space
Classic Information Retrieval (IR) relied on Boolean logic and TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency). Does the document contain the term? Yes/No. How often?
Modern search operates in High-Dimensional Vector Space. Google converts your content (and the user’s query) into “embeddings”—numerical vectors representing semantic meaning.
-
The Problem: You can have perfect “On-Page SEO” (H1, Title, Keywords) and still fail because your content’s vector direction is misaligned with the query’s vector.
-
Our Approach: We don’t just optimize keywords. We use internal Python-based NLP models to calculate the Cosine Similarity between your page and the high-confidence cluster of current top rankers. If your semantic angle is strictly orthogonal (irrelevant) to the core entity cluster, no amount of backlinks will save you.
2. The “Twiddler” Architecture: Why Good Sites Drop
One of the most critical concepts for modern SEOs—confirmed by patent analysis (US Patent 20170068711A1) and leaked API documentation—is the “Twiddler” framework.
In Google’s pipeline, there is a distinction between the Initial Retrieval (Ascender) and the Re-Ranking (Twiddler) phases.
-
Retrieval: Finds the most relevant documents based on IR scores.
-
Twiddlers: Lightweight re-ranking functions that apply multipliers or demotions after the initial fetch.
A Twiddler might look like this in pseudocode: final_score = initial_ir_score * quality_boost * freshness_demotion
The Agency Insight: Many “SEO mysteries” are simply Twiddlers in action. Your page has high textual relevance (high IR score), but a Navboost Twiddler demotes it because user interaction signals (clicks, dwell time) from the last 30 days fell below the expected probability threshold. We audit specifically for these post-retrieval signals, ensuring your site survives the re-ranking filters.
3. Optimizing for “Information Gain” (Patent US20200349150A1)
Google is actively fighting “consensus content”—articles that simply rehash what is already in the top 10 results.
A pivotal patent describes a scoring system based on Information Gain. The engine asks: Does this document provide new information vectors not present in the other documents the user has already seen?
If your strategy is “Skyscraper Content” (making a longer version of competitors’ posts), you might actually be triggering a redundancy filter.
The YourDigitalWeb Methodology: We use entity extraction to map the “Proposition Density” of the SERP.
-
Step 1: Map all entities covered by competitors.
-
Step 2: Identify the “semantic void” (what is missing?).
-
Step 3: Engineer content that injects unique data points or perspectives. This increases the probability of your document being selected to satisfy the diversity requirements of the algorithm.
4. The “Multi-Armed Bandit” Testing
Have you noticed your rankings bouncing from position 3 to 8 and back to 4 within a week? This is likely not a penalty; it is an Exploration vs. Exploitation test (often modeled as a Multi-Armed Bandit problem).
Google allocates a percentage of traffic to “explore” new or updated pages to gather data.
-
Deterministic View: “My rankings are unstable! Panic!”
-
Probabilistic View: “Google is testing my confidence interval. I need to stabilize user signals.”
We advise clients not to react impulsively to these variances. Making drastic changes during a Bandit test resets the confidence score, effectively forcing the algorithm to start learning your page from scratch.
Engineering Confidence
In a probabilistic environment, you cannot guarantee a result. But you can mathematically maximize the probability of a positive outcome.
Stop asking: “Why isn’t this ranking #1?” Start asking: “How can we increase the confidence score of this URL’s vector embedding while minimizing the risk of a Quality Twiddler demotion?”
This is not magic. It is Information Retrieval engineering. And it is exactly what we do at YourDigitalWeb.